Arm, the company that designs the processors used in many of the world’s smartphones and other mobile devices, has announced its latest generation of CPU cores. The new cores include a flagship Cortex-X4 core, a Cortex-A720 performance core, and a Cortex-A520 efficiency core. These cores are designed to deliver a significant performance boost over previous generations, while also improving efficiency. The new cores are based on Arm’s latest Armv9.2 architecture. And they support a wide range of new features, machine learning, and cryptography.
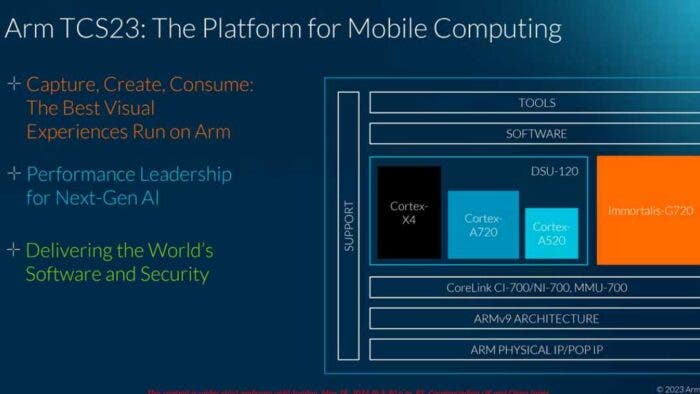
Arm’s CPU cores for 2023
Although Arm doesn’t produce SoCs by itself, it offers a Total Compute Solution (TCS) platform as a reference design to help manufacturers create their own chip implementations. This year’s Total Compute Solution is called TCS23. It includes three levels of CPU cores: the Cortex-X4, Cortex-A720, and Cortex-520. Each core is designed for a different type of workload, and they can work together to provide a complete system solution.
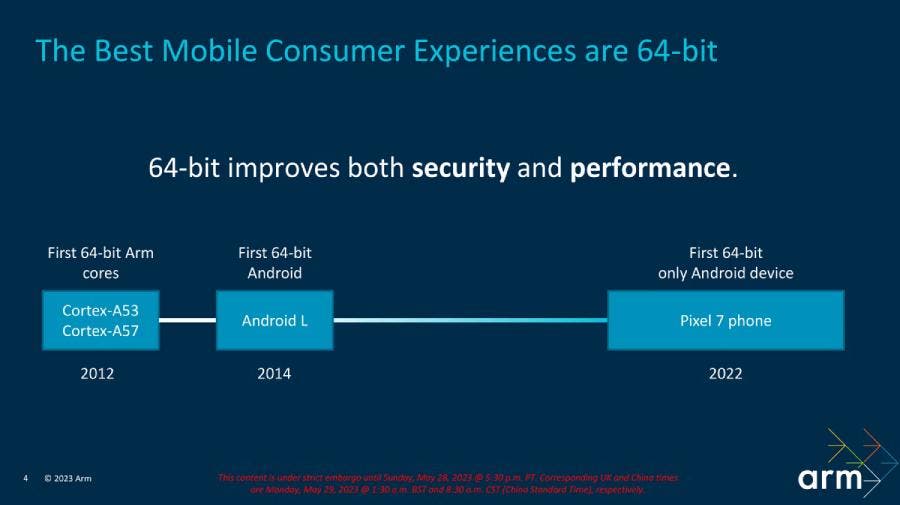
Before discussing the performance and efficiency gains of these cores, it’s important to note a significant change in TCS23. This year ARM has made a major change to its CPU structure. All new cores will be 64-bit only, and there will be no 32-bit revisions. This means that all future high-end smartphone chipsets and Arm SoCs in other segments, like laptops, will be 64-bit only.
This change may seem drastic, but it has been in the works for some time. Arm has been gradually phasing out 32-bit support in its latest cores, and Google has been encouraging developers to update their apps to 64-bit for several years. Now it looks like the 32-bit Android is finally at the end of the road.
Arm Cortex-X4 CPU Core
Now, let’s dive into the flagship Cortex-X4. Architecturally, it is similar to last year’s X3. And it can run at the same frequencies as last year’s cores, but it will use up to 40% less power. It is also less than 10% larger in physical size and the most efficient Cortex-X core ever built.
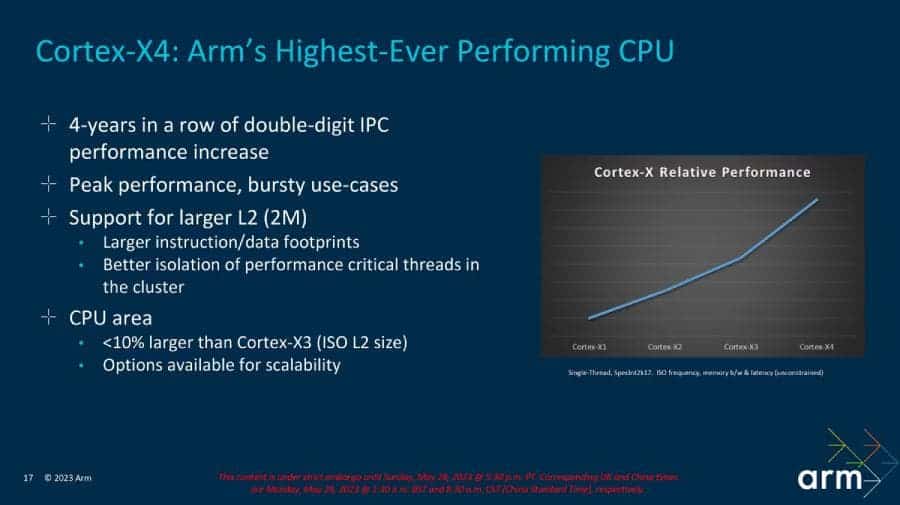
The X4’s performance improvements come from a number of front-end and back-end changes. In the front end, Arm improved branch prediction, which can be costly if it is incorrect. Arm also promises that a 2MB L2 cache will yield higher performance in real-world usage.
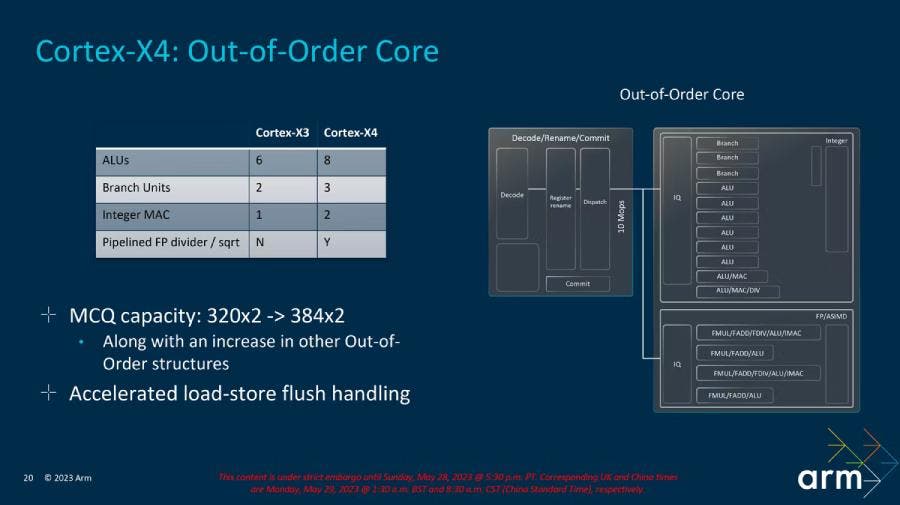
Moreover, the X4 core has more Arithmetic Logic Units (ALUs), a branch unit, and a Multiply-Accumulator unit. It also pipelines floating point and square root operations.
In the back end, load-store address generation has been increased from 3 instructions to 4 per cycle, and the translation look-aside buffer in L1 has been doubled. All of these changes result in an average of 15% performance improvement with the Cortex-X4.
Cortex-A720
While X-series cores are designed for high performance, the A-series cores generally balance out the power and performance. And the Arm’s new Cortex-A720 is no expectation.
Gizchina News of the week

The new Cortex-A720 CPU core is 20% more power efficient than last year’s Cortex-A715 core. It can also provide 4% more performance for the same power consumption. This is due to a number of design changes, including shorter and more efficient pipelines, and a new spatial-prefetch engine.
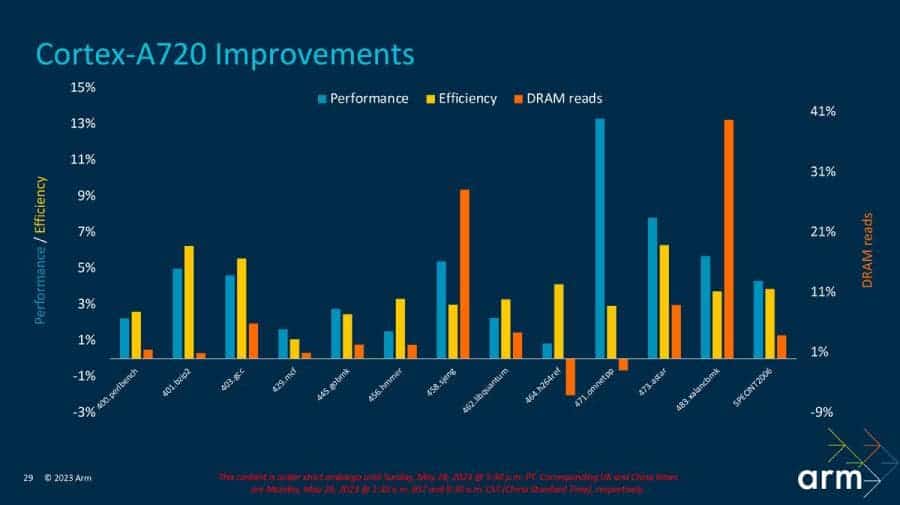
Arm has also made it possible to implement the Cortex-A720 in a variety of sizes. The smallest configuration is the same size as the Cortex-A78 core and it will still provide 10% more performance and all of ARMv9’s security features. Of course, this smaller configuration is not ideal for smartphones. But it could be useful in other devices where silicon area size is a limiting factor.
Cortex-A520
Lastly, Arm’s CPU announcement includes the Cortex-A520 core. While the X series focuses on raw computational power and the A7xx series balances computational needs and power draw, the A5xx series is optimized for long battery life. Like the Cortex-A720 and Cortex-X4, the A520 is also a 64-bit-only core.
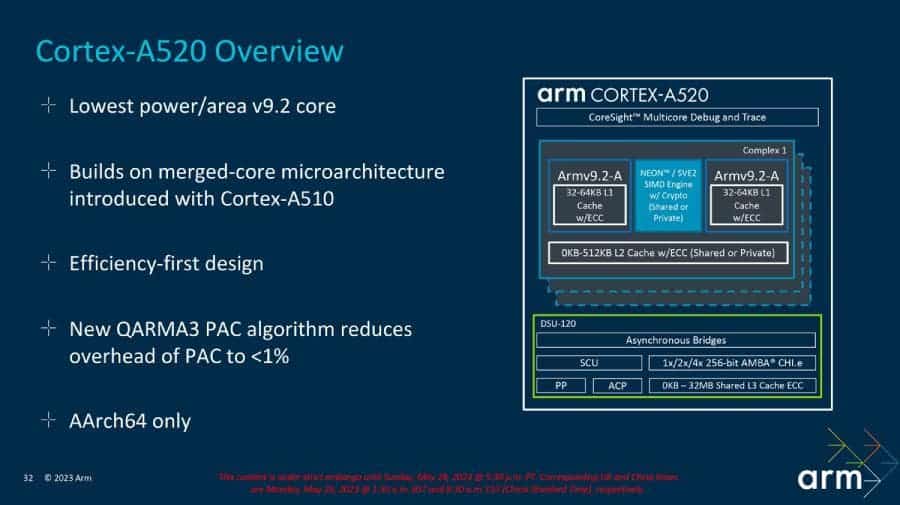
Arm says it is 22% more efficient than the previous generation A510 core. Arm has achieved this efficiency by removing one ALU unit. However, the engineers have also made improvements to the data prefetch and cache, which has allowed them to claw back 8% more average performance.
DymaicIQ
Arm’s DynamIQ Shared Unit (DSU) is a critical component of any chip that uses Arm’s core designs. It integrates one or more cores with an L3 memory system, control logic, and external interfaces in order to form a multicore cluster. This allows all of the cores to communicate with each other and share resources, which is essential for performance and efficiency.
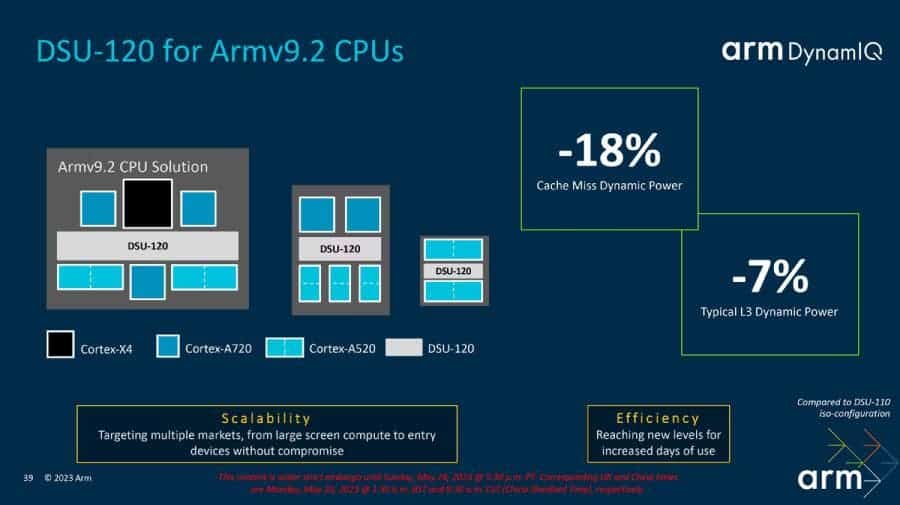
The latest version of the DSU, DSU-120, offers a number of improvements over the previous version, DSU-110. These improvements include support for up to 14 cores per cluster, up to 32MB of L3 cache, and improved efficiency in a number of key areas. These improvements will benefit the entire chip, but they will have a particularly positive impact on power consumption and efficiency.
Final Words
These 64-bit Armv9.2 CPUs will be the building block for flagship SoCs from Snapdragon, MediaTek, Samsung, and more. Arm’s internal testing showed that the new CPUs offer significant performance and efficiency gains in a 1+5+3 core layout. However, chip manufacturers will choose their own CPU layouts, which may affect performance and efficiency.
Based on past trends, we can expect to see smartphones powered by SoCs with Arm’s new cores by the end of this year. Arm also announced an updated Immortalis-G720 GPU alongside the new CPUs.